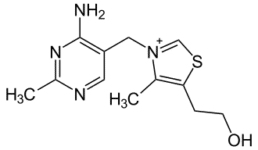
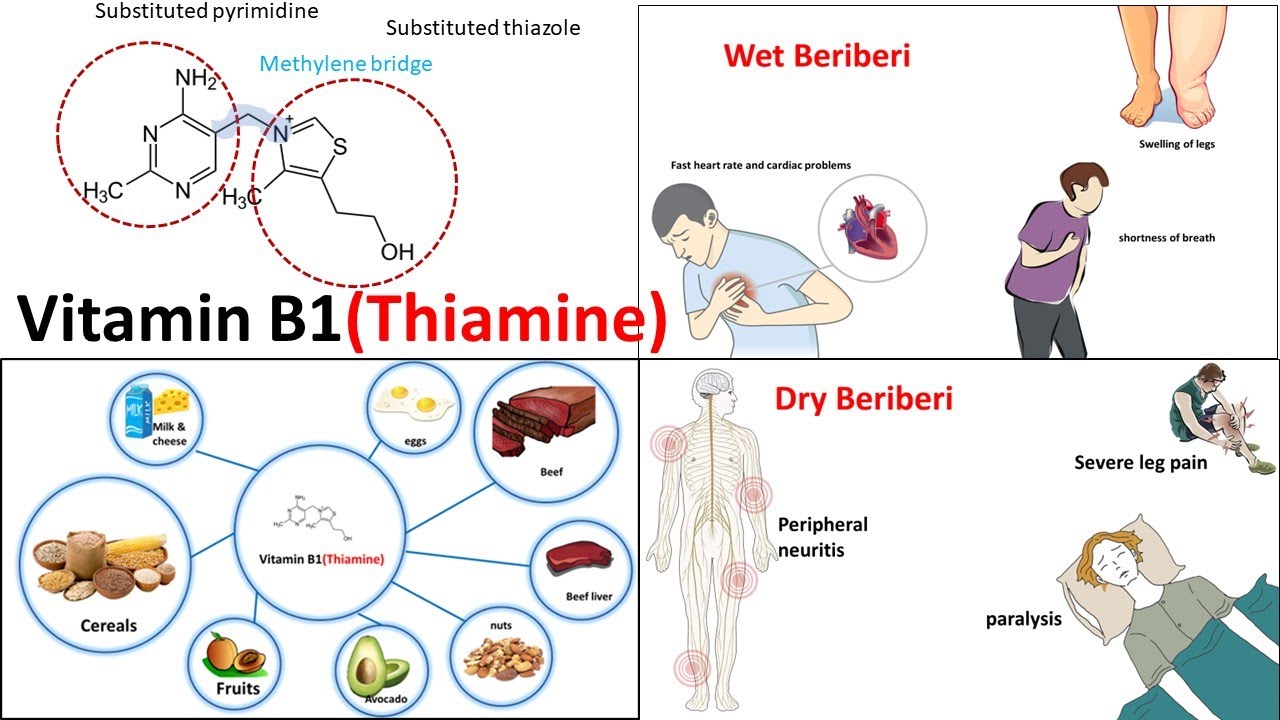
Thiamine Molecular Structure
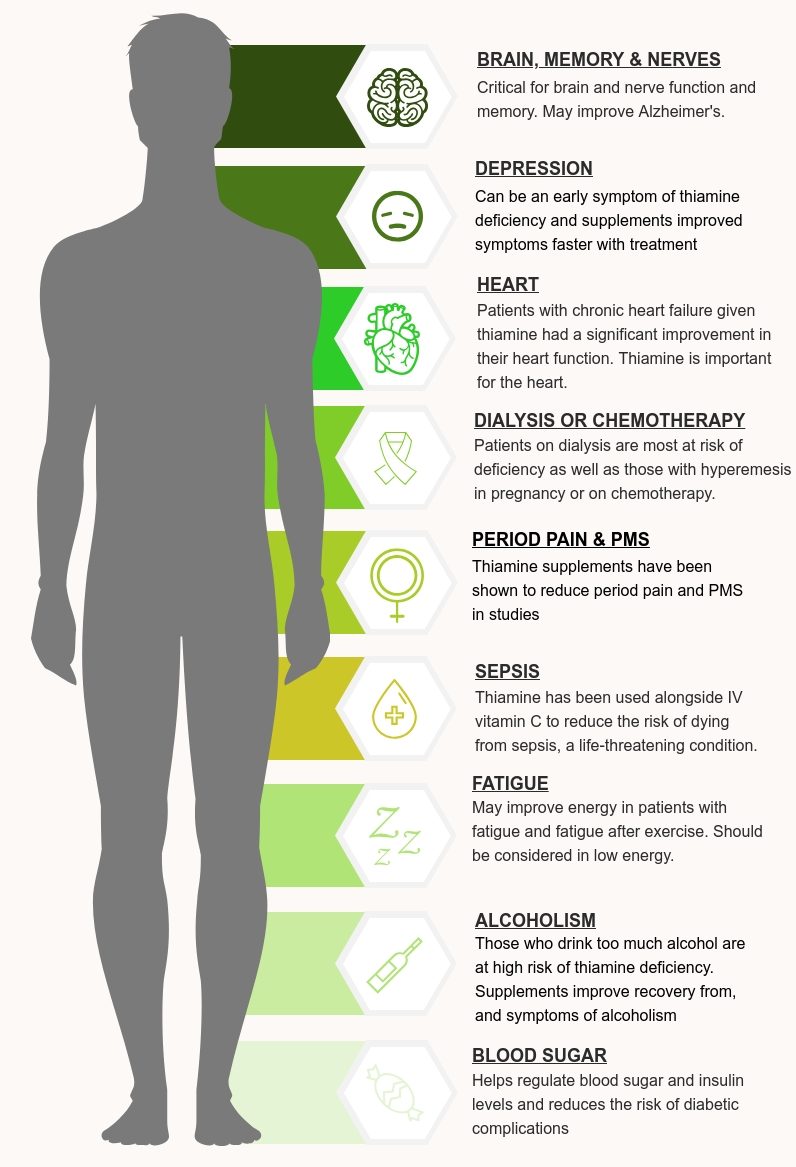
Thiamine or Vitamin B1 is a water-soluble B vitamin with many nervous system benefits. All B vitamins help the body convert carbohydrates into glucose, which is used to produce energy. B vitamins, referred to as B complex vitamins, also help the body metabolize fats and protein. B complexes are needed for healthy skin, hair, eyes, and liver. They also help the nervous system function properly and are essential for proper brain function. Most people are not deficient in B1 although alcoholics, people with Crohn’s disease, diabetics, sufferers of anorexia, and those undergoing kidney dialysis may be deficient. Symptoms of thiamine deficiency are fatigue, irritability, depression and abdominal discomfort, high blood sugar and trouble digesting carbohydrates. The technical term for Vitamin B1 deficiency is Beriberi.
If you have undergone gastric bypass surgery then you need to be aware of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome. Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome a/k/a Wernicke’s Encephalopathy is a serious disease caused by a Vitamin B1 deficiency that often involves significant and permanent brain damage. This condition commonly develops after a patient undergoes gastric bypass surgery or any other procedure or medical condition in which a patient is deprived of Vitamin B1 and the doctor and/or a subsequent emergency room doctor fails to recognize the signs and symptoms of Wernicke’s Encephalopathy until it is too late to reverse the process. Hence, if you have had gastric bypass surgery, this is one nutrient you’ll probably want to bolster with supplementation. This is especially true if you experience any of the following symptoms: loss of appetite, fatigue (tiredness), irritability, nerve damage, tingling in your arms and legs, blurry vision, nausea and vomiting, and delirium. It is important to recognize these symptoms early to prevent permanent damage to the brain and nervous system.
Other conditions resulting in an increased requirement for this nutrient include: strenuous physical exertion, fever, pregnancy, breast-feeding, and adolescent growth. Such conditions place individuals with marginal intake at risk for developing symptomatic deficiency.
Women who are pregnant or lactating require more of this nutrient due to its being preferentially sent to the fetus and placenta, especially during the third trimester. For lactating women, it will be delivered in breast milk even if it results in a deficiency in the mother. Pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarum are also at an increased risk of deficiency due to losses when vomiting. This nutrient is important for not only mitochondrial membrane development, but also synaptosomal membrane function. It has also been suggested that a deficiency plays a role in the poor development of the infant brain that can lead to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
The Health Benefits of Thiamine:
AGING
• May prevent the Cross-Linking of proteins caused by excess glucose.
• The brain’s store declines with age, so supplementation by the aging may prevent some aspects of brain aging.
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
• May help to prevent Atherosclerosis.
• Can improve Blood Circulation.
• Beneficial in both Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) and Cardiomyopathy as it increases left ventricular ejection fraction.
• Can help to prevent Heart Attack and Stroke.
• Myocardial Ischemia may be reduced by supplementation.
• Required by the Heart to maintain normal muscle tone.
• Helps with the production of red blood cells.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
• Loss of appetite can occur as a result of deficiency.
• Colitis and Constipation can be caused by deficiency.
• Facilitates the production of Hydrochloric Acid in the Stomach.
• Required for normal Muscle tone of the Stomach and Intestines.
• Nausea may be caused by deficiency.
HEARING / VISION
• Required for normal functioning of the Acoustic Nerve.
• May help to prevent Cataracts.
• Glaucoma patients are often found to be deficient.
• Optic Neuritis may be caused by deficiency.
IMMUNE SYSTEM
• Many Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) patients have been found to be deficient and this deficiency contributes to the Central Nervous System (CNS) impairment that occurs in AIDS patients.
• Through its role in Detoxification, Thiamine may help to prevent the following Cancers:
▪ Cervical
▪ Colon
▪ Laryngeal
▪ Prostate
METABOLISM
• Helps treat Lactic Acidosis.
• Can enhance Athletic Performance.
• Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) patients have been found to be deficient.
• Cirrhosis patients have low levels and is often recommended for this condition.
• Retards the Cross-Linking of proteins, a significant part of aging.
• Required for proper functioning of the Krebs Cycle.
• Reduces Lactic Acid.
• Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 & 2 patients have found that Benfotiamine (a fat-soluable form of this vitamin) to be beneficial due to its ability to inhibit the Cross-Linking of the body’s endogenous proteins.
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
• May improve the effectiveness of NSAIDS for the treatment of Backache.
• Muscle Weakness can occur as a result of deficiency.
• Deficiency can cause Muscle Atrophy.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
• Can alleviate Adrenal Insufficiency as a result of surgery.
• Aggressiveness can result from deficiency.
• May reduce the craving for alcohol.
• Useful in Alzheimer’s Disease by facilitating the release of Acetylcholine.
• Low levels accelerate the formation of Amyloid-Beta plaque in the brain.
• Anorexia Nervosa may occur from deficiency.
• Anxiety and Depression may result from deficiency.
• Deficiency may be implicated in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
• Beriberi is the classic symptom of deficiency.
• High concentrations are found in the brain and are required for optimal functioning of the Blood-Brain Barrier.
• Poor Concentration and/or Confusion may result from deficiency.
• Headaches can occur as a result of low levels.
• May protect the brain from Alcohol-Induced damage.
• Low levels can lead to Insomnia.
• Deficiency can lead to Lowered Intelligence, Irritability, Decreased Learning Ability, Memory Impairment (short and long term) and Mood Disorders.
• Neuropathies and Neuralgia may be improved through supplementation.
• Numbness in the Hands and Feet can occur from deficiency.
• Optic Neuritis can be improved by supplementation.
• Burning Tongue Syndrome and Mouth Ulcers can occur as a result of deficiency.
SEXUAL SYSTEM (Female)
• The pain of Dysmenorrhea can be alleviated by supplementation.
• Deficiency increases the risk of Miscarriage.
SEXUAL SYSTEM (Male)
• May be useful in the treatment of Male Impotence.
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) Benefits
Thiamine Deficiency
USAGE
Thiamine is best taken with meals and is generally well tolerated even at high doses. Since this nutrient is water soluble it is best to spread out your total daily dosage throughout the day as opposed to taking a single large dose.
My Personal Recommendation:
Receive my personal support with each verifiable purchase made through this site.
Get answers to your questions either by
email or telephone.
Take advantage of my 35 plus years of experience as a researcher and healer.
Just use the CONTACT form to initiate the process.